How to import data into R using RStudio from files stored in local directories, using absolute and relative file paths
Links to topics on this page
- RStudio’s default working directory
- Use an absolute file path
- Use a relative file path
- Using a project in RStudio to locate and find files
- Getting and setting the working directory
- Get the file path of a file in Windows
RStudio’s default working directory
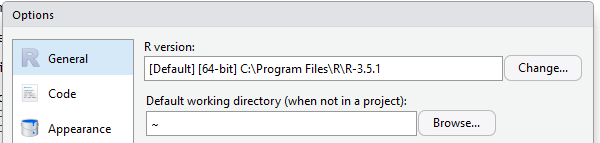
When you install RStudio, it creates a default working directory, where it assumes files are going to be located. You can customize this location via Tools|Global Options, or in individual files — see below.
Importing data into R using an absolute path
To copy the path of a file in Windows, see the note below.
Key point
If we copy the file path of a file in Windows and paste it in to our R code ‘as is’, there is a problem with the backslash ‘\’ file path separators. This is because in R the backslash ‘\’ is the ‘escape’ character — R interprets the symbol as an escape character not as a backslash.
# file path copied and pasted from Windows Explorer
C:\Users\Documents\R\R examples\long-data.csvTo fix this, options include:
- adding an extra ‘\’ to each instance of the backslash (i.e. use a backslash to escape the backslash), or
- replacing the backslashes with a forward slash ‘/’ (shown in the code block below).
# filepath using '\' separators
> dt1 <- read.csv("C:\Users\Documents\R\R examples\long-data.csv")
Error: '\U' used without hex digits in character string starting ""C:\U"
> head(dt1)
Error in head(dt1) : object 'dt1' not found
# filepath using '/' separators
> dt1 <- read.csv("C:/Users/Documents/R/R examples/long-data.csv")
> head(dt1)
Year Rank Value
1 1990 Low 98
2 1991 Low 45
3 1992 Low 81
4 1993 Low 56
5 1994 Low 49
6 1995 Low 100The main drawbacks of using absolute file paths are:
- if you share files, another user won’t have the same directory structure as you, so they will need to recreate the file paths;
- if you alter your directory structure, you’ll need to rewrite the paths;
- an absolute file path will likely be longer than a relative path, more of the backslashes will need to be edited, so there is more scope for error.
Importing data into R using a relative path
This example assumes you’re not running an R (.r or .R) file via a Project in R (see the option described below).
We have an R file saved in a sub-directory, along with a csv file in the same directory, that we want to import data from. However, our default working directory is at a different location.
# file paths for our R file and the csv we want to import from
C:/Users/Documents/R/R examples/filepaths.r
C:/Users/Documents/R/R examples/long-data.csv
# the default working directory in RStudio
C:/Users/Documents/If we try to import the csv file by using only the filename, RStudio can’t find the file, even though it’s in the same directory as the R file that we’re running. RStudio is looking for the csv in the ‘working directory’.
We have to use an identifier to tell RStudio where to find the csv file RELATIVE to the working directory — the identifiers ‘~’ and ‘.’ both work.
# RStudio can't find the csv file as it's looking in the default working directory
> dt <- read.csv("long-data.csv")
Error in file(file, "rt") : cannot open the connection
In addition: Warning message:
In file(file, "rt") :
cannot open file 'long-data.csv': No such file or directory
# RStudio finds the file if we use the relative reference '.'
(and remember to use forward slashes in the file path)
> dt1 <- read.csv("./R/R examples/long-data.csv")
> head(dt1)
Year Rank Value
1 1990 Low 98
2 1991 Low 45
3 1992 Low 81
4 1993 Low 56
5 1994 Low 49
6 1995 Low 100
# use the relative reference '~'
> dt2 <- read.csv("~/R/R examples/long-data.csv")
> head(dt2)
Year Rank Value
1 1990 Low 98
2 1991 Low 45
3 1992 Low 81
4 1993 Low 56
5 1994 Low 49
6 1995 Low 100Using a project in RStudio to locate and find files
If you work in a project in RStudio, and keep all related files in one directory, then you can refer to files using only their file names — no file paths are needed. The working directory is automatically set to the project directory.
You can also use sub-directories within your main project directory, e.g. for ‘data’, ‘r’ etc. and use relative file paths.
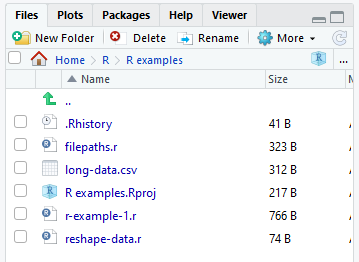
Working in a project has various other benefits too — you can easily navigate to all project files in the ‘Files, Plots, Packages…’ pane, and if you’re publishing to shinyapps you’ll want all your files in one place.
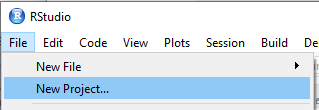
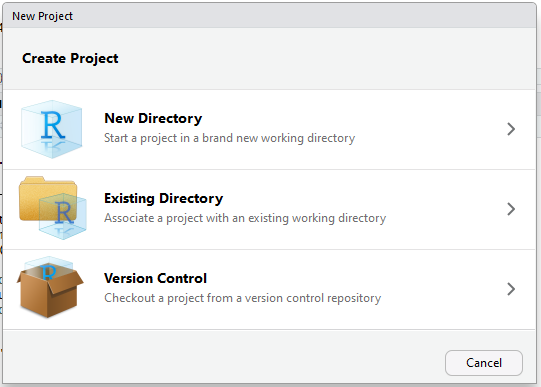
To create a New Project in RStudio, select File | New Project… and you can either start from scratch in a new directory, or select an existing directory where you’ve already started to store your project files.
Getting and setting the working directory
One option to manage access to local files is to set the location of the current working directory, either on a temporary basis per file, or set the default directory via global options:
- getwd() returns the file path location of the current working directory
- setwd() sets the current working directory temporarily
- in RStudio’s Global Options, set the default working directory.
# get the file path of the current working directory using getwd()
Note that R uses forward slashes in the file path.
> getwd()
[1] "C:/Users/Documents"
# set the location of the current working directory using setwd()
> setwd("C:/Users/Documents/R")
> getwd()
[1] "C:/Users/Documents/R"
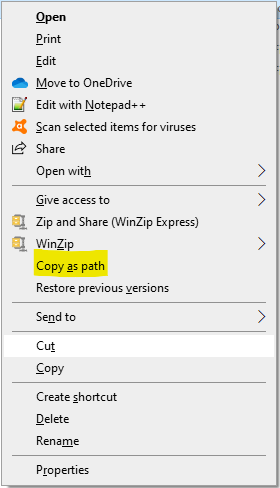
Copy a file path in Windows
- In Windows Explorer, browse to the file that you want the file path to.
- Hold down the Shift key and Right-click on the file name.
- In the pop-up context menu, click on the option to ‘Copy as path‘.